Announcement:
Asia-Pacific Forest Invasive Species Network Training Workshop
PINEWOOD NEMATODE COLLABORATIVE: HOW TO IDENTIFY, DETECT, AND MANAGE PINEWOOD NEMATODE
13-18 September, 2020, Nanjing, China
Background
Worldwide, forests and forest plantations are facing new and increasing threats from insects and diseases. In some cases, the annual tree mortality caused by insects and diseases can far exceed other threats such as fire or floods. Apart from economic losses, these threats also pose negative consequences to the environment and native habitats. In an effort to address these problems, several training workshops have been recently held under the umbrella of the Asia-Pacific Forest Invasive Species Network (APFISN), for example, the APFISN Training Workshop on Forest Invasive Pests, held in Haikou, Hainan, China in 2016 and another APFISN Training Workshop, Developing Skills in Forest Protection: An Integrated approach, was held in Beijing, China in 2018. The focus of these and other previous workshops was to provide a general working knowledge of the identification, survey and management of forest insects and diseases and weeds. Although useful, these particular workshops did not focus on a specific pest.
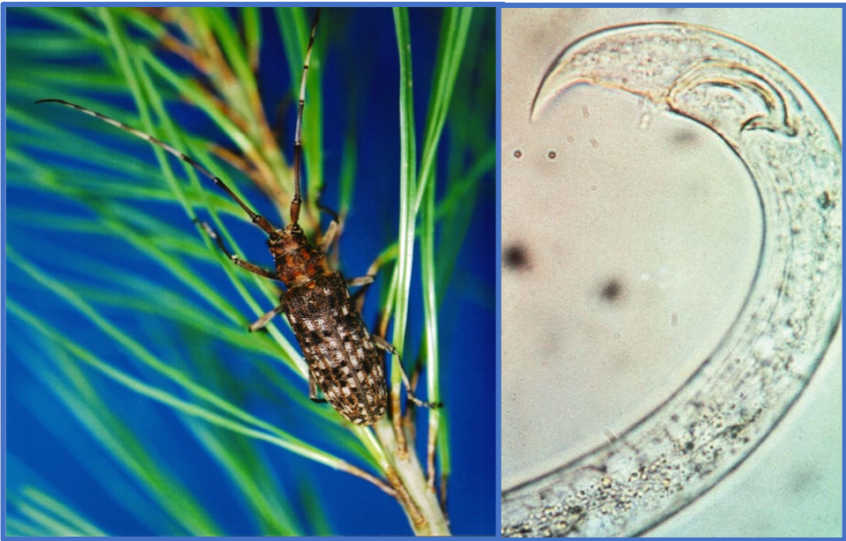
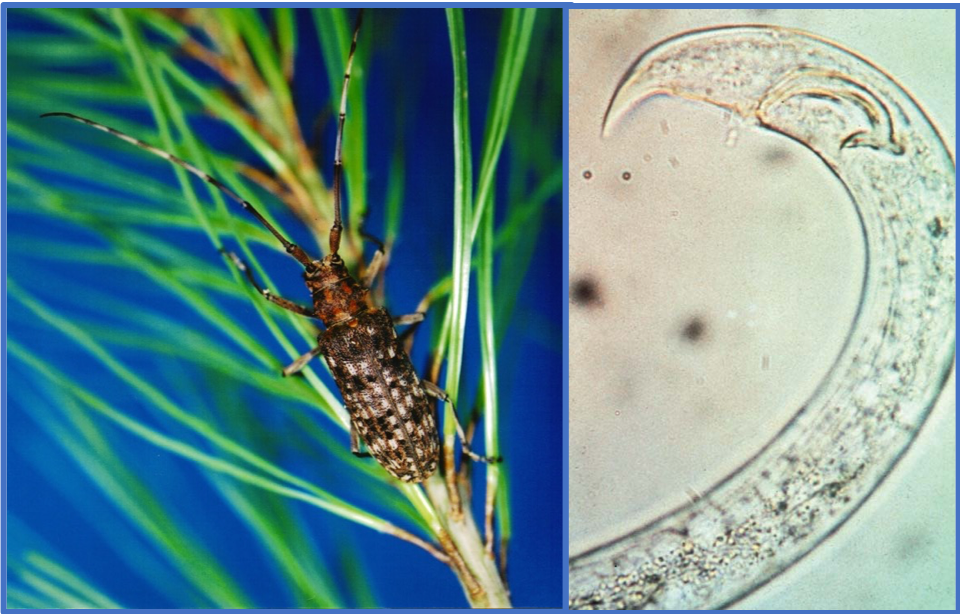
Over the last two decades, pinewood nematode (PWN – Bursaphelenchus xylophilus), a destructive disease of pine forests, has caused significant mortality to many pine forests in northeast Asia and southern Europe prompting a global quarantine alert, which is affecting international trade. Pinewood nematode is vectored by cerambycid beetles (Monochamus spp.), which are therefore the causal agents for spreading pine wilt disease (PWD). As with many forest pests, especially pathogens, damage is often cryptic and resources are limited so delineating and ascertaining the true cause is difficult. Prompt detection of pine wilt disease is especially challenging since PWN lives and reproduces within tree resin ducts and the tree does not show symptoms until it is almost dead. As more research is conducted and experience gained by affected countries, valuable tools are being developed to help survey, identify, and manage PWN. Even with this significant progress, there is still much more work to do in order to successfully manage PWD. It is under this situation that APFISN is supporting an informal Pinewood Nematode Collaborative where interested countries and entities can participate to share research and experiences and work together to find viable solutions to the damage caused by PWN.
As part of the PWN Collaborative, APFISN and its partners are sponsoring a training workshop to be held at Nanjing Forestry University, Nanjing, China from September 13-18, 2020, which, aims to provide hands-on training on properly identifying PWN based on signs and symptoms and DNA analysis; survey methods; and best management practices for PWN control. It is targeted at recent upper level graduates, and mid-level practitioners who are involved in forestry management, forest health monitoring, and management of forest diseases and their control, particularly PWN. There will also be a one day forum to share and discuss operational management experiences of PWN between affected countries and interested entities.
The co-hosts include the Asia-Pacific Forest Invasive Species Network (APFISN), International Society of Zoological Sciences (ISZS) and Nanjing Forestry University. The supporting partners are FAO, the USDA Forest Service, the State Forestry and Grassland Administration of China, and the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Science.
Objectives
The main objectives of this training workshop are to equip participants with the skills to:
1. Recognise and identify the main signs and symptoms of PWN damage in the field.
2. Detect and diagnose PWN using various methods of sampling, culturing, specimen preservation and collection, especially using DNA techniques.
3. Understand current and suitable methods of PWN management and control with emphasis on integrated pest management (IPM).
Participants
This training course is targeted at recent upper level forestry graduates and practitioners who plan to/will be involved in aspects of forest health and management, monitoring, silviculture, tree breeding, pest and disease management and control, especially PWN. The target number of trainees is 15 participants. The number of participants from Asia-Pacific Forestry Commission member countries outside China will be selected depending on the available budget and relevance to PWD situation in their respective countries.
Working Language
The working language for the symposium and training course is English.
Location
The training will be held at the Forest Pathology Laboratory and on the grounds of Nanjing Forestry University (NFU), Nanjing, China. During the training, visits will be made to Nanjing Forestry University pathogen collection to view the large collection of tree disease samples, and the nearby PWD infected forest for disease survey, sample collection, and on-site discussion and design of disease management and control methods.
Outcomes
Participants will be exposed to the current state of knowledge of PWN, including an overview of basic biology and life cycle, disease survey and sampling methods, recognition of signs and symptoms caused by PWN, diagnosis especially through the use of DNA techniques, laboratory techniques such as culturing, making slides, usage of microscopes, and principles of PWN management and control, including integrated pest management (IPM). Apart from the hands-on training, participants will also be provided with basic resources, reference material, web-links, contacts, and other tools so that they can apply what they have learned at the workshop back in their home countries.
Nominations for Training Course Participants
Participants should have an understanding of pathology so they are at least familiar with general terms and biology of pathogens. Participant’s work should also be directly related to forest diseases or DNA analysis. Participants must submit a nomination form (below) to be considered for this training. Participation from APFISN partner countries already affected by PWD or at threat from its introduction will be prioritised (e.g. Vietnam, Phillipines, Republic of Korea, Democratic People’s Republic of Korea)
Meeting organizers will cover selected participant’s air travel (direct round-trip economy class), registration and visa fees, and hotel accommodation and meals during the meeting in Nanjing, China from 13-18 September, 2020.
Completed nomination forms (click here to download) are DUE at the APFISN Beijing Secretariat before May 11, 2020.
![]() PWN WORKSHOP 2020 Announcement
PWN WORKSHOP 2020 Announcement
Completed forms and inquiries should be sent to Dr. Jacob Wickham, at the APFISN Secretariat–Beijing: jacobwickham@ioz.ac.cn.
Contact
Dr. Jacob Wickham (jacobwickham@ioz.ac.cn), APFISN Beijing Office or ISZS Secretariat. Address: Room C-506, Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 1 Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing 100101, China; Tel: +86-010-6480-7295; Fax: +86-010-6480-7295; Email: jacobwickham@ioz.ac.cn; Website:www.globalzoology.org.